A nuclear stress test plays a significant role in diagnosing cardiac arrhythmia, a type of. This diagnostic tool provides essential information about the heart and its blood vessels blood vessels, helping doctors to accurately determine the underlying cause of arrhythmia.
The nuclear heart scan is a minimally invasive procedure that uses small amounts of radioactive material, called tracers, to produce images of the heart's blood flow and function. The tracer is injected into the bloodstream and accumulates in areas with high blood flow, allowing doctors to visualize the blood flow through the heart's chambers and coronary arteries.
During a nuclear heart scan, the patient is typically expected to run on an exercise bike to increase their heart rate and blood pressure. This allows the doctor to evaluate the heart's performance under stress, which can help identify areas of reduced blood flow or damaged heart tissue that may be contributing to arrhythmia.
The scan produces photos of the heart in multiple positions, including rest and exercise, allowing doctors to compare the data and identify any areas of abnormal blood flow or cardiac function. The images are then analyzed using advanced computer software to produce a comprehensive analysis of the heart's performance.
One of the key benefits of a nuclear heart scan is its ability to detect areas of destroyed or scarred heart tissue, اسکن هسته ای which can be a common cause of cardiac arrhythmia. The scan can also detect coronary artery disease, which can lead to poor circulation to the heart and arrhythmia. By providing a clear picture of the heart's functioning, the nuclear heart scan helps doctors to develop an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan for patients with cardiac arrhythmia.
In addition to its diagnostic utility, the nuclear heart scan is also a valuable tool for assessing the effectiveness of treatments for cardiac arrhythmia. Patients who have undergone medical or surgical treatment for arrhythmia may require a follow-up nuclear heart scan to assess their heart function and ensure that the treatment is working as intended.
In summary, the nuclear heart scan is a crucial diagnostic tool for identifying and managing cardiac arrhythmia. Its ability to produce detailed images of the heart's blood flow and function, combined with its minimally invasive technique, make it an essential component of arrhythmia diagnosis and treatment. By providing a clear picture of the heart's health, the nuclear heart scan helps doctors to develop successful treatment plans and improve patient results.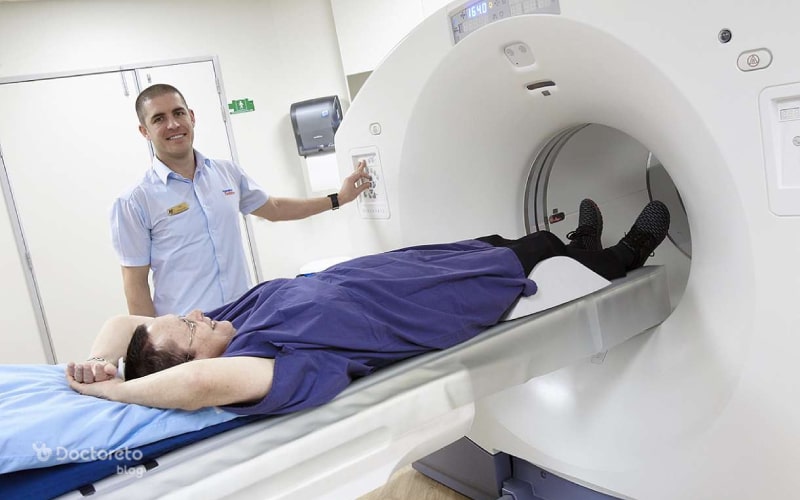
The nuclear heart scan is a minimally invasive procedure that uses small amounts of radioactive material, called tracers, to produce images of the heart's blood flow and function. The tracer is injected into the bloodstream and accumulates in areas with high blood flow, allowing doctors to visualize the blood flow through the heart's chambers and coronary arteries.
During a nuclear heart scan, the patient is typically expected to run on an exercise bike to increase their heart rate and blood pressure. This allows the doctor to evaluate the heart's performance under stress, which can help identify areas of reduced blood flow or damaged heart tissue that may be contributing to arrhythmia.
The scan produces photos of the heart in multiple positions, including rest and exercise, allowing doctors to compare the data and identify any areas of abnormal blood flow or cardiac function. The images are then analyzed using advanced computer software to produce a comprehensive analysis of the heart's performance.
One of the key benefits of a nuclear heart scan is its ability to detect areas of destroyed or scarred heart tissue, اسکن هسته ای which can be a common cause of cardiac arrhythmia. The scan can also detect coronary artery disease, which can lead to poor circulation to the heart and arrhythmia. By providing a clear picture of the heart's functioning, the nuclear heart scan helps doctors to develop an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan for patients with cardiac arrhythmia.
In addition to its diagnostic utility, the nuclear heart scan is also a valuable tool for assessing the effectiveness of treatments for cardiac arrhythmia. Patients who have undergone medical or surgical treatment for arrhythmia may require a follow-up nuclear heart scan to assess their heart function and ensure that the treatment is working as intended.
In summary, the nuclear heart scan is a crucial diagnostic tool for identifying and managing cardiac arrhythmia. Its ability to produce detailed images of the heart's blood flow and function, combined with its minimally invasive technique, make it an essential component of arrhythmia diagnosis and treatment. By providing a clear picture of the heart's health, the nuclear heart scan helps doctors to develop successful treatment plans and improve patient results.


댓글 달기 WYSIWYG 사용